Overview
-
- Overview
- Assessment Framework
Assessment Framework
The attitude toward mathematics and mathematical practice competence refer to experience of joy in mathematics when participating in mathematical activities individually or with peers based on a passion for mathematics. “Attitude” means experiencing the joy of mathematics by having interest, self-efficacy, and meta-affect in mathematics, and having a passion for mathematics through perseverance and challenge. “Practice” means engaging with society through mathematics by resolving conflicts and collaborating with peers to practice mathematics together, enjoying mathematical culture, and displaying global citizenship based on this attitude. Accordingly, “attitude and practice” can be manifested through practicing mathematics with the right attitude.
One’s attitude toward mathematics consists of two aspects: the experience of joy in mathematics and a passion for mathematics. The joy of mathematics can be realized through interest, self-efficacy, and meta-affect, and a passion for mathematics is categorized into perseverance and challenge.
While a student’s attitude reveals their psychological and personal aspects, practice reveals the social and cultural aspects perceived by the student. Practice is classified into mathematics considering interactions with others and mathematics sharing mathematical culture and participating in various community or group activities.
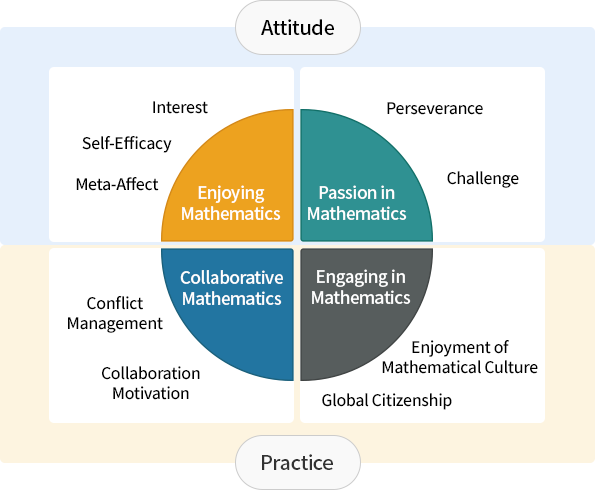
The assessment components
The results of this test will tell you about your type for the eight components of assessment and the level of global citizenship. The components of assessment are categorized as follows.
| Component | Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interest | Interest in mathematics or mathematics learning you find enjoyable or fun in a situation involving mathematics | Situational interest | Interest that activates the joy experienced in a mathematics learning situation | |
| Academic interest | Interest that activates the joy and fun of mathematics | |||
| Self-efficacy | Belief in your perceived ability to effectively perform a set of behaviors related to mathematics and execute the process | Performing task efficacy | Belief in your ability to select appropriate methods and use strategies required in the process of solving mathematical tasks | |
| Self-regulated efficacy | Belief in your ability to select and use learning methods suited to you in mathematics learning and control your behavior in the learning process | |||
| Meta-affect | Tendency to aware, evaluate, regulate, and use your emotions in learning mathematical concepts or solving problems | Affective awareness | Tendency to be aware of your own emotions when learning mathematics or solving problems | |
| Affective evaluation | Tendency to evaluate whether your emotions are good or bad in the view of mathematics learning when learning mathematics or solving problems | |||
| Affective Regulation | Tendency to regulate your emotions in a positive way when learning mathematics or solving problems | |||
| Affective Uilization | Tendency to plan studying mathematics for the future based on your emotions when learning mathematics or solving problems | |||
| Perseverance | Tendency to continue trying instead of giving up on your goals or interests in mathematics learning or task performance | Maintaining passion | Tendency to persistently maintain goals or interests by maintaining your passion for mathematics learning or tasks | |
| Continuing effort | Tendency to continue trying despite failures, frustrations, or adversities encountered in the process of achieving your goal | |||
| Challenge | Attempting to develop your own abilities or confirm your performance without avoiding difficulties when solving mathematical tasks | Pursuing development | Attempting to develop your mathematical skills and make progress in learning | |
| Pursuing achievement | Attempting to confirm your mathematical ability or be acknowledged by achieving your goal | |||
| Conflict management | Tendency to select and utilize strategies to resolve conflicts that occur when conducting mathematical activities in collaboration with friends | Avoiding expressions of stance | Avoiding conflicts | Strategy to avoid conflict situations as much as possible for your own peace and stability |
| Pursuing relationships | Strategy to not express your goal or stance by attaching the most importance to maintaining good relationships with friends | |||
| Pursuing expressions of stance | Pursuing goals | Strategy to express your goal or stance to resolve a conflict situation even at the cost of your relationships with friends | ||
| Collaborative problem solving | Strategy to adequately achieve your goals or needs while maintaining good relationships with other parties | |||
| Collaboration Motivation | Desire to solve mathematical tasks in collaboration with friends | Completing tasks | Desire for ultimate satisfaction in solving a task | |
| Expressing your knowledge and abilities | Desire to show other students that you know what they do not | |||
| Taking the initiative in group activities | Desire to take the initiative and lead other students in the direction you want to go | |||
| Being faithful to your role within the group | Desire to meet the expectations of other members by fulfilling your role in the group | |||
| Enjoyment of mathematical culture | Ability to perceive the value of mathematics; have an interest in mathematical culture and mathematics associated with history, philosophy, and the arts; enjoy participating in mathematics-related activities; and share and relate to mathematical culture | Perceiving the value of mathematics | Perceiving the mental disciplinary, practical (or utilitarian), aesthetic, and cultural values of mathematics based on an understanding of the essence of mathematics and mathematical thinking | |
|
(Mathematics associated with history, philosophy, and the arts) Having an interest in mathematical culture |
Having an interest in the history of mathematics (mathematicians and mathematics-related discoveries and inventions), mathematical philosophy, mathematical heritage, mathematics-related performing arts (theater, music, and dance), mathematics-related visual arts (architecture, film, and art), mathematics-related literature (fiction, essays, and poetry), etc. | |||
| Enjoying participating in mathematics |
Using mathematics-related cultural facilities (exhibition halls, experience centers, and libraries related to mathematics) Participating in mathematical cultural events (mathematics lectures and camps) Participating in mathematics-related group activities |
|||
| Sharing and relating to mathematical culture | Sharing the mathematical culture you experienced in everyday life or in the media and relating to other people’s mathematical culture | |||
| Global citizenship | Ability to act fairly and responsibly through mathematical activities in relation to problems occurring in real-world contexts as a member of the global community. Ability to respect the perspectives of others, present opinions based on logical grounds, and have and practice the attitude of making rational decisions | Acting fairly and responsibly | Acting fairly and responsibly as a global citizen based on the process and outcomes of learning mathematics | |
| Respecting the perspectives of others | Respecting the perspectives of others with various backgrounds in politics, economy, society, culture, religion, history, and the environment based on the process and outcomes of learning mathematics | |||
| Presenting opinions based on logical grounds | Understanding problem situations that occur in real-world contexts based on the process and outcomes of learning mathematics and presenting opinions based on logical grounds | |||
| Making rational decisions | Understanding problem situations that occur in real-world contexts based on the process and outcomes of learning mathematics and making rational decisions | |||
